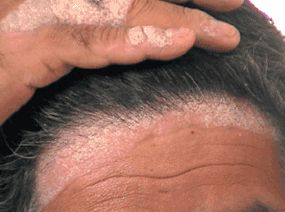
 Scalp psoriasis is a non-contagious disease that affects the skin on the scalp, and it appears as reddish and raised patches that are often scaly. This skin disorder can appear as a single patch or multiple patches, but it can also affect the entire scalp and even spread to areas on the forehead, behind ears, and the back of the neck.
Scalp psoriasis is a non-contagious disease that affects the skin on the scalp, and it appears as reddish and raised patches that are often scaly. This skin disorder can appear as a single patch or multiple patches, but it can also affect the entire scalp and even spread to areas on the forehead, behind ears, and the back of the neck.
Unfortunately, the exact cause of scalp psoriasis or other types of psoriasis is yet to be determined. Doctors agree that it is most likely caused by a disorder in the immune system that leads to cells growing much faster than normal and building up into patches. Another aspect of scalp psoriasis that specialists agree on is the fact that a family history of psoriasis increases one’s chances of developing it.
Psoriasis is not limited only to the scalp of patients and it can affect any skin surface. In the U.S., around half of patients affected by this disease have it on the skin of their scalp. This skin disorder can be unnoticeable and mild, without causing the patient any major discomfort. In severe cases, however, scalp psoriasis can last for a long time and it can be very itchy, which can affect patients’ sleep and day-to-day life.
Scratching the crusted sores can cause skin infections and even hair loss. Hair loss is not caused by the disease itself, instead hair loss is caused by intensive scratching, certain treatments for psoriasis or even the stress associated with this disease. Hair loss is not permanent, and once the disease clears, lost hair will grow back.
Patients with a severe case of scalp psoriasis feel a sensation of intense itching and burning, have a dry scalp, which is covered with thick, scaly or red patches.
The treatment for psoriasis includes topical creams, oral medication, phototherapy and ultraviolet light. Topical treatments like creams, oils, soaps, ointments and shampoos contain either salicylic acid or coal tar. These can be purchased over-the-counter or your dermatologist can give you a prescription. Sometimes doctors inject steroids directly into the affected areas. If this or topical treatments fail to clear the disease, phototherapy (with our without lasers) or UV lights may be recommended for patients.
These treatments are often used for dealing with a milder form of the disease. When dealing with severe psoriasis, patients are prescribed oral medications such as corticosteroids, Vitamin A (derivative), Vitamin D (derivative), cyclosporine, and methotrexate. These strong medications can have serious side effects so patients are kept under observation. Derivatives of Vitamin A and D are not the same as the regular vitamin supplements, which unfortunately are not efficient against the disease.
In the absence of a targeted cure, it is hard to efficiently deal with the effects of psoriasis. The above-mentioned treatments can help manage the symptoms and prevent the reoccurrence of the disease. Fortunately, continuous research into the causes of the disease leads to the emergence of new types of treatments. Biologics are a newly developed medication that tries to combat the disease by preventing the skin from producing too many cells. For now, patients can get these by injection or IV.